An Integrated Approach in Management of Pemphigus Vulgaris
Abstract
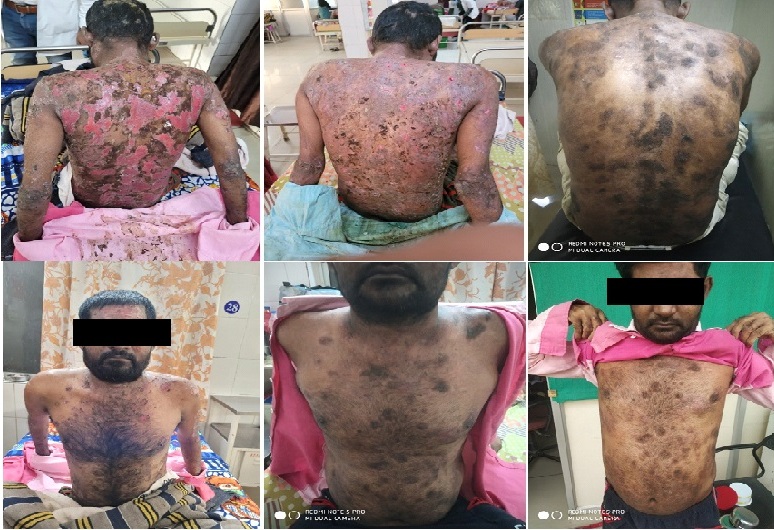
Pemphigus refers to a group of autoantibody-mediated intra-epidermal blistering diseases characterized by loss of cohesion between epidermal cells (a process termed acantholysis). Applying pressure to the skin of these patients may elicit the separation of the epidermis which is known as Nikolsky’s sign. Pemphigus vulgaris can be compared with Agnivisarpa based on similar manifestation. The mainstay of treatment is systemic glucocorticoids in allopathy science. The current mortality is around 5% with glucocorticoids treatment. Case History: This case report is of 40 years old male patient who presented with blisters formation on whole over body, perspiration, itching and burning since last 6 months. He was treated in indoor department with Snehana Cikitsa mainly along with oral glucocorticoids for 25 days. The dose of oral glucocorticoids was tapered with improvement in patient’s condition. Result: At the time discharge, patient was prescribed 10mg prednisolone and oral Ayurvedic medicines. After 25 days of treatment patient had more than 90% relief and glucorticoids was stopped. On the 2nd follow of treatment patient was kept only on Ayurvedic medicines. During first two follow-ups, patient had significant relief.
Downloads
Copyright (c) 2023 International Journal of Ayurveda and Pharma Research

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.






