Assessing the Effect of Shodhana (Purification) Process by Triphala Decoction on Shilajit Using High Performance Thin Layer Chromatography
Abstract
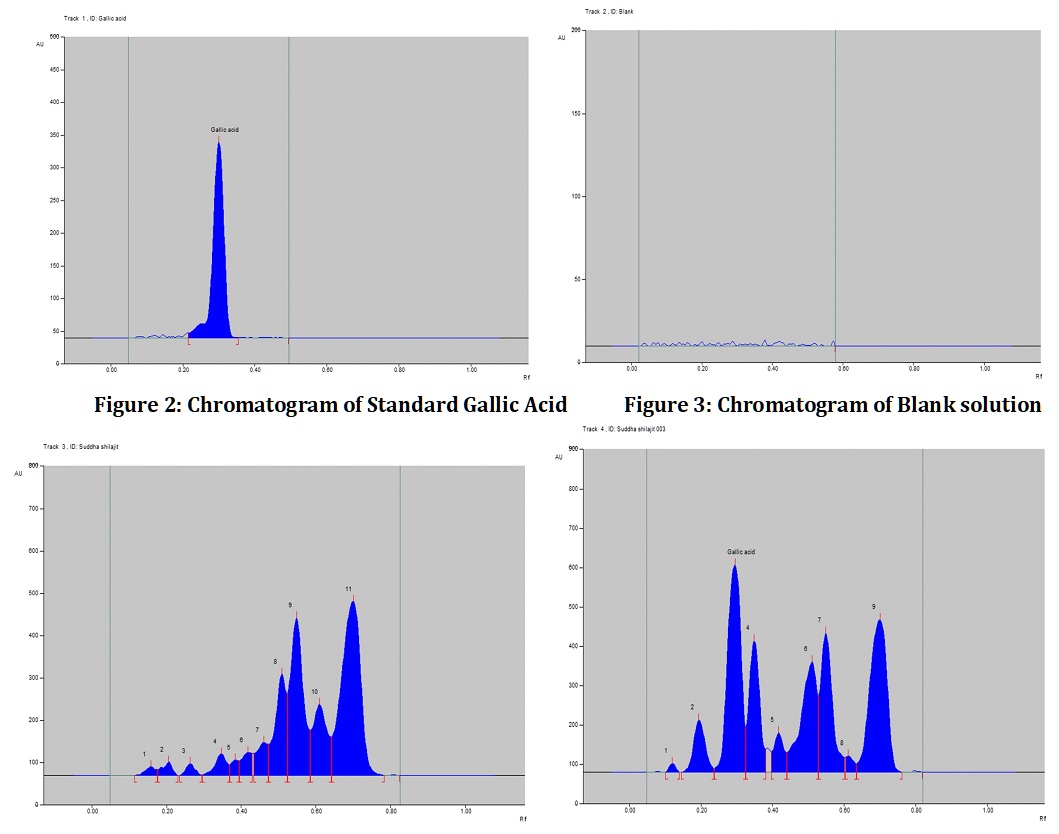
Standardization of Shodhit Shilajit is a major challenge. Objective: Objective of the present study was to assessing the effect of Shodhana purification process on Shilajit as well as assessing the difference in fingerprint of raw Shilajit and Shodhit Shilajit by HPTLC and physicochemical tests. Methods: The standardization parameters such as appearance, identification of active marker compound Gallic acid and Fingerprint comparison by HPTLC, Physicochemical test parameters like loss on drying, pH value, ash value, water soluble extractive, ethanol soluble extractive and assay of humic acid and fulvic acid were evaluated during the study. Chromatographic separation was achieved by using Toluene: Ethyl acetate: Formic acid (5.0:4.0:1.0 v/v/v) as mobile phase followed by comparing the Rf values. Results: The presence of active marker compound gallic acid in Shodhit Shilajit was confirmed by comparing the Rf value with standard. HPTLC fingerprint also confirmed that constituents from raw Shilajit transferring to the Shodhit Shilajit after the process of Shodhana. Total Ash value and Acid insoluble ash value reduced from 52.95% to 21.67% and 2.35% to 0.39% respectively while Water soluble extractive value increased from 59.33% to 72.13% after Shodhana process. There is also an increase in percentages of humic acid and fulvic acid from 7.10% to 8.23% and 36.91% to 50.12 % in Shodhit Shilajit. Conclusion: All these results showed the significance and effectiveness of Shodhana process in reducing the impurities and ultimately enhancing the therapeutic activity of Shodhit Shilajit. These evaluation parameters can be used for the standardization of Shodhit Shilajit and also can be routinely employed for analysis in Quality Control Lab.
Downloads
Copyright (c) 2024 International Journal of Ayurveda and Pharma Research

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.






