Effect of Prathimarsa Nasya and Abhyanga on the Physical Fitness among Athletes in the Sports Hostel of Mar Basil Higher Secondary School Kothamangalam
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.47070/ijapr.v12i1.3074Keywords:
Physical fitness, Dinacharya, Abhyangam, Prathimarsa nasyaAbstract
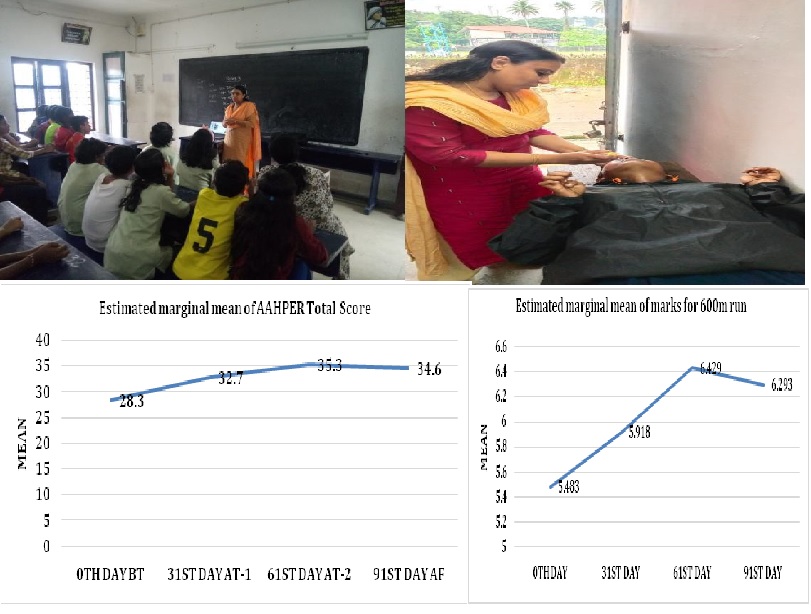
Physical fitness has direct influence on athlete’s performance level. Sports medicine deals with the physical fitness and the treatment of injury related to sports and exercise by curative, rehabilitative and preventive modalities. Ayurveda the complete science of life can contribute in this field also. Abhyanga and Prathimarsa nasya are important Dinacharya procedures which play a key role in the maintenance of health and fitness of athletes. Regular Abhyanga controls Vata dosas and improves physical strength. Prathimarsa nasya improves the musculature of neck shoulder and chest. Ayurveda classics advice Abhyanga with Thila thailam and Prathimarsa Nasya with Anuthailam as a daily regimen for healthy individual. This study is being made to highlight the application of these Ayurveda Dinacharya procedures in promoting the physical fitness of sports persons. This study is a single group pre-post study. 47 subjects of age group 12–18 participating in athletic events were selected from the Sports Hostel of Mar Basil Higher Secondary School Kothamangalam as per the inclusion and exclusion criteria. After necessary investigations participants had been advised to follow the daily regimen Abhyanga with Thila Thaila after work out, half an hour before bath and Prathimarsa Nasyam with Anuthailam in morning, between 6am- 6.30am for 60 days continuously. Assessments were done on 31st day, 61st day and 91st day (follow up). Scores recorded for test items were converted into marks as per formula based on AAHPER fitness test chart and subjected to statistical analysis using repeated measure ANOVA test. Results showed that Pratimarsha nasya and Abhyanga have statistical significance in improving the physical fitness variables and overall performance level of athletes.
Downloads