Anthelmintic Activity of Methanolic Extract of Leaves Of Cyclea Peltata Lam and it’s Statistical Analysis
Abstract
The aim of this research is to develop a safe and effective anthelmintic from plants, due to the resistance and toxic effect of synthetic anthelmintics on animals and humans. There are several side effects for synthetic drugs including drug resistance, toxicity, and drug residual in animal products. So there is a need for the exploration of medicinal plants for the treatment of different types of worm infections.
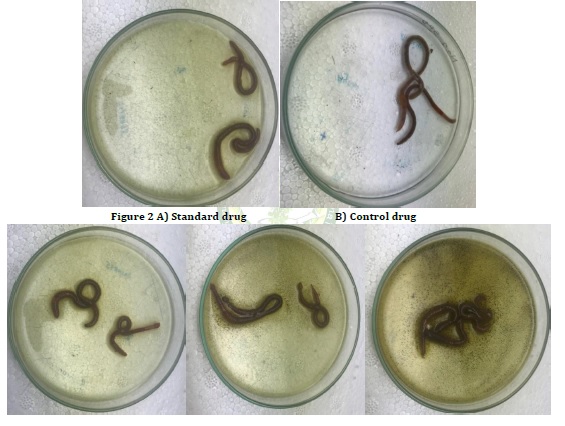
In this research a medicinally and traditionally important plant is used, leaves of Cyclea peltata Lam. The methanolic extract of the leaves were prepared by maceration technique and are monitored for the anti-helminthic activity against adult Pheretima posthuma worms. The reason for selecting this plant is due to the presence of tannins, which have been proved by previous phytochemical studies. Tannins have the capability to bind free proteins in the cuticle, oral cavity of helminths, thus causing the death. Albendazole (25 mg/5ml) is used as a controlled drug by using the adult motility assay method. Three concentrations were prepared (25, 50, and 100mg/5ml). The time required for the immobility and death of the worms were determined. This study deals with the statistical analysis by one way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test at 95% confidence interval using graph pad prism software version 9.0.0 reveals the result that the methanolic extract of the Leaves of Cyclea peltata Lam causes the immobility and death of the vermicular in a concentration-dependent manner as compared to the standard drug Albendazole.
Downloads
Copyright (c) 2023 International Journal of Ayurveda and Pharma Research

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.






