A Comparative Clinical Study of Trikarshika Kwatha with and without Lifestyle Modification in the Management of Vatarakta with Special Reference to Hyperuricaemia
Abstract
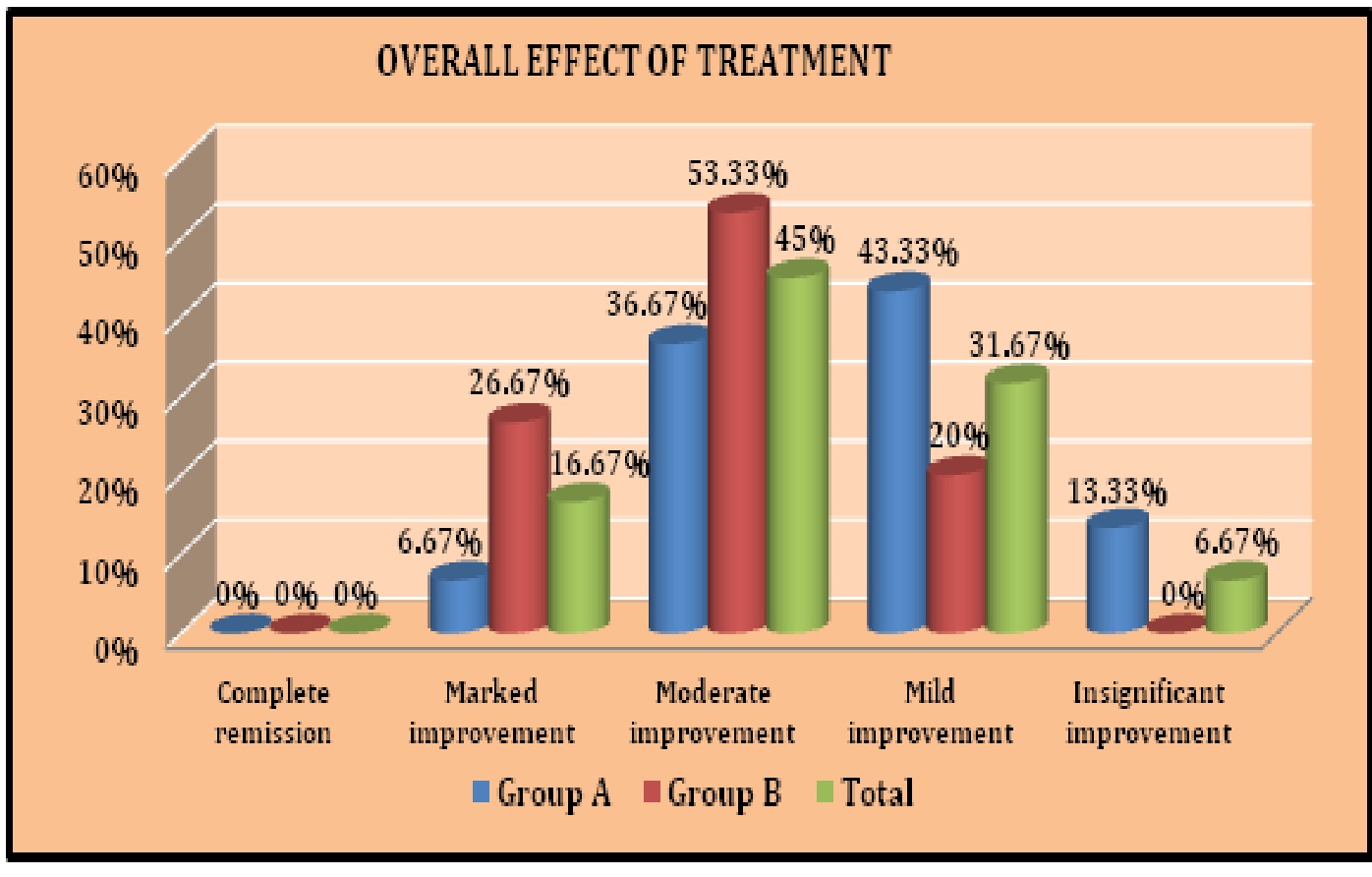
Nowadays, people are more vulnerable to metabolic disorders due to their faulty dietary and behavioural habits. One such disorder is Vatarakta which causes functional impairment due to involvement of Sandhi (joints). It is manifested by Ruk, Toda, Sparsha asahatva, Shopha, Raga, Daha and Stabdhata in Sandhi. Vatarakta can be correlated with Hyperuricaemia or Gout due to similarity in their clinical features. Hyperuricaemia is defined as abnormally high level of uric acid in blood (i.e. >6mg/dl in female and >7mg/dl in male). On the other hand, Gout is an inflammatory response to monosodium urate crystals formed secondary to hyperuricaemia. Aims and objectives: 1. To evaluate the effectiveness of Trikarshika kwatha and lifestyle modification in the management of Vatarakta. 2. To compare the effects of Trikarshika kwatha with and without lifestyle modification in the management of Vatarakta. Materials and methods: Raw herbs of the research formulation were collected after proper identification and Kwatha was prepared for oral administration. For the clinical study, total 60 patients were selected on the basis of selection criteria. Selected patients were randomly divided into two groups. (i) Group A: 30 patients were treated with Trikarshika kwatha. (ii) Group B: 30 patients were treated with Trikarshika kwatha along with Lifestyle modification. Individual patient was treated for 45 days along with follow up at the interval of every 15 days. To assess the effectiveness of treatment, scoring pattern was followed for subjective and objective parameters. They were assessed before and after treatment. The collected data were analysed statistically by using Paired t-test. Results: On the basis of all statistical data, it can be said that patients of Group B showed better results in all parameters in comparison to patients of Group A. Conclusion: Both Trikarshika kwatha and Lifestyle modification are affective but Trikarshika kwatha with Lifestyle modification is more effective than Trikarshika kwatha without Lifestyle modification in the management of Vatarakta.
Downloads
Copyright (c) 2021 International Journal of Ayurveda and Pharma Research

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.






