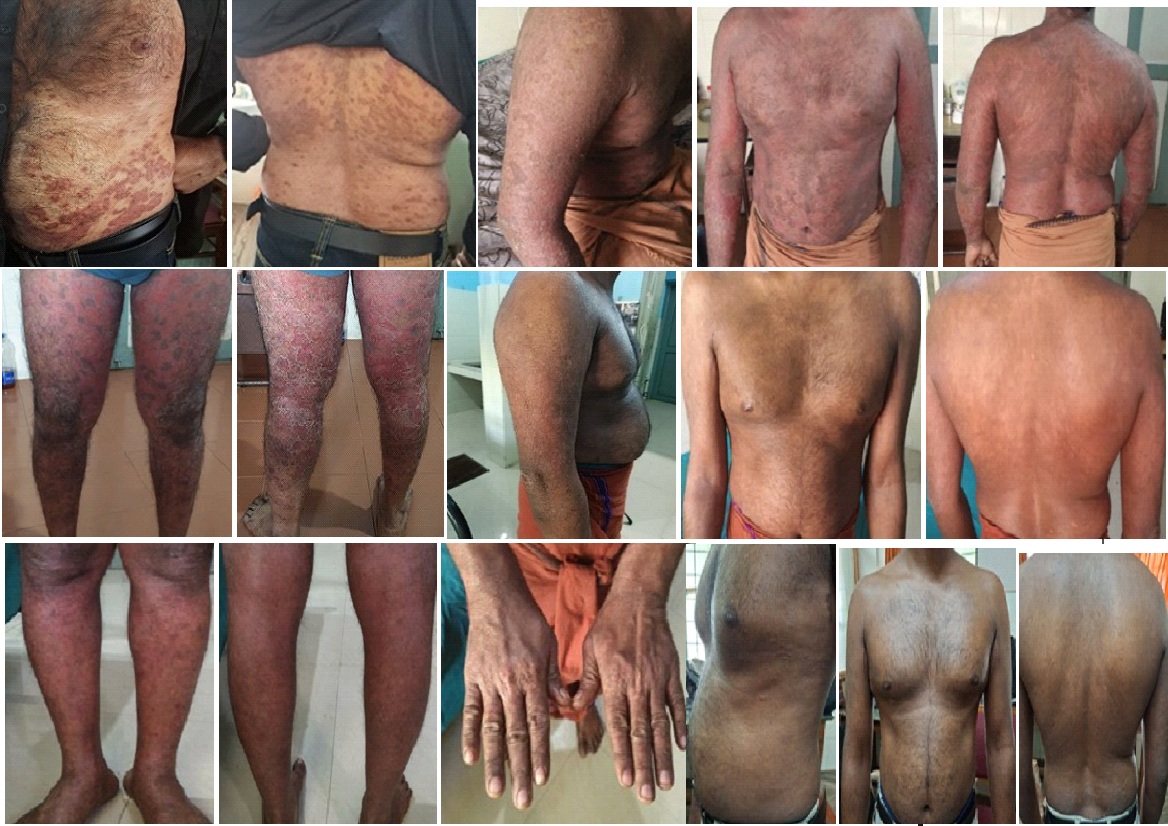
Ayurvedic Management of Sidhma Kushta: An Evidence Based Case Report
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.47070/ijapr.v13i3.3624Keywords:
Psoriasis, Sidhma kushta, PASI Score, Ayurvedic managementAbstract
Alteration to the typical skin texture causes mental and physical discomfort for any individuals. There are several skin diseases which affect the person’s psychological status and disturb the social life. Among those conditions psoriasis is most common, the worldwide prevalence of psoriasis is about 2%, but varies according to regions. Psoriasis is a papulosquamous skin disease, was originally thought of as a disorder primarily of epidermal keratinocytes, but is now recognized as one of the commonest immune-mediated disorders. Sidhma kushta is an ayurvedic classification of skin diseases that shares similar symptoms and characteristics. Ayurveda offers a well-defined treatment protocol after analysing the vitiated Dosha and Dooshya. The treatment includes Deepana, Paachana, Shamana, Sodhana and Rasayana. Along with that, patient strictly followed proper Pathyas and avoided all the Apathyas. Takradhara, Snehapaana and Virechana along with external applications gave significant improvement in patient’s condition. With the increasing demand for Ayurvedic intervention in psoriasis management, establishing an evidence-based protocol is essential. This case study provides a systematic assessment for evaluating ayurvedic treatment and employs the Psoriasis Area Severity Index (PASI) score to measure improvements in skin conditions. On follow up total appearance of the skin found to be improved and patient’s symptoms reduced well.
Downloads