Pharmacognostical Study of Leaf of Hamsapadi (Adiantum Lunulatum)
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.47070/ijapr.v10i12.2638Keywords:
Adiantum lunulatum, Hamspadi, authentication, Microscopy, Macroscopy.Abstract
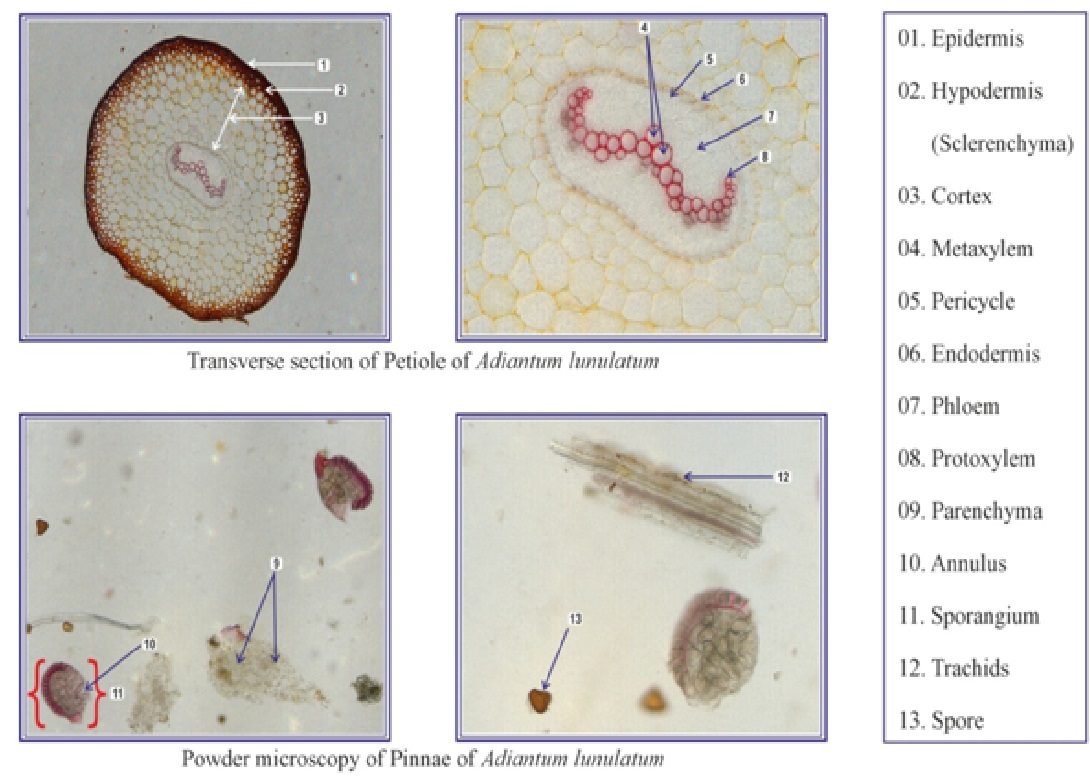
Pharmacognostical evaluation of leaves of Adiantum lunulatum is done for identification in field and for differentiation from other species of Adiantum. Methods: A detailed literary work of drug studied and its pharmacognostical, phytochemical and analytical study including powder microscopy and taste determination of leaves with suitable instruments. Results: Macroscopic evaluation reveals the pinnacles are half moon shaped, alternate, sub-opposite or opposite in apical portion of the frond, having lobes with minor incisions. In microscopic structure the two surfaces of pinna are covered by epidermis and epidermal cells are wavy in outline. The opening and closing of stomata will be regulated by guard cells, whereas there is absence of stomata on epidermis. The vascular cells are lined by an endodermal tissue. Transverse section of petiole showed that it is externally covered by an epidermis lined by cuticle on its outer wall which renders the petiole to be shining. Below the epidermis is a fairly thick hypodermis made up Sclerenchyma cells of 4-5 layers in thickness. They are dead cells compact in arrangement and look dark in colour. Powder microscopy of leaves reveals shows few Tracheids of the veins and the Parenchyma cells of the leaves. The Sori are very prominent structures occurring at the leaf margin, they are visible characteristically under the microscope. The Sori contain number of Sporangia each Sporangium is lined by cells with U shaped thickening having their outer wall thin in nature. Conclusion: This study will help in Authentication of Hamspadi plant.
Downloads